It’s time to rest.
That is how houseplants feel in winter.
Some houseplants go dormant in winter when the temperature drops and there is less sunlight. You need to provide some water to keep the houseplants alive. You’ll notice houseplants go dormant when they start dropping leaves as the weather gets cold.
In this post, I’ll help you recognize when your houseplants go dormant, what you can do to take care of them during this stage. I’ll also give some tips on how to prevent dormancy from happening in your plants.
Let’s begin.
Do houseplants go dormant in winter?
Houseplants detect the onset of winter when there is a drop in temperature levels and less availability of natural light. The stress from these environmental changes and the often drastic reduction in humidity from heating systems will activate plants into a dormant state.
During this period, some plants will drop their leaves and become dormant with no signs of growth, or they might slow down significantly, displaying less new growth.
Yes, house plants do indeed go dormant in the winter.. They do this in order to prepare the plants soft tissue for incoming sub-zero temperatures, water & nutrient shortages or even just dry weather. The plants know not to waste energy by attempting to grow when the environment does not suit, instead they converse this energy until the more favourable conditions return. – Leslie Vincent, Horticulturalist, Atkins Garden Center
Stressful conditions such as little or no water may cause houseplants to go dormant to conserve any water that may still be left. The plant may seem like it is dying, but this is just a defense mechanism to keep alive while waiting for more suitable growing conditions.
Dormancy is crucial for survival, allowing rest while conserving energy and nutrients required for future growth.
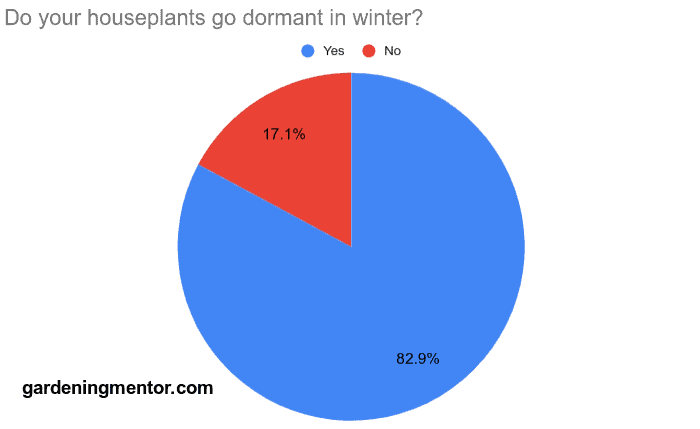
I asked fellow gardeners if they found their houseplants go dormant in winter and what they do to take care of them. 82.9% responded that their houseplants went dormant.
Why do houseplants go dormant in winter?
Plants go dormant in winter because they are affected by changes in temperature and light. Shorter days and longer nights result in less amount and quality of light as sunlight gets less intense.
By entering into a state of dormancy, plants prepare their soft tissue to withstand the freezing temperatures, dry weather conditions, shortage of water and nutrients they will experience during the harsh winter.
Plants conserve energy and use the stored sugars and carbohydrates produced during their growing season to survive the winter. They remain rested while they wait for warmer temperatures which will bring renewal and new growth.
How can you tell if a houseplant is dormant?
Even though the leaves of houseplants often become yellow due to lack of water, and some even drop their leaves in winter and appear to be dead, there are methods of telling if the plant is still alive by conducting natural tests such as:
Use the scrape test on the houseplant
Scrape away a portion of the outer layer of skin on the stem with your fingernail or a sharp knife. If the underneath is green and damp, the plant is still alive, but it might be dying or already dead if it is brown and difficult to scrape.
To test further for signs of life, scrape a bit lower down the stem, and if this appears to be green, then the plant is viable and can be trimmed down to just above the green area.
Use the snap test on the houseplant
Bend the tip of the stem or branch. If it is flexible or cracks open and the tissue is green or white, the plant is alive and dormant. A twig that snaps off easily could be dead, but to be certain, try the scrape test to see if the lower part of the stem is still alive.
Check the roots of the houseplant
Remove the plant from the pot and check if the roots are light in color, supple, and full of moisture. If they are dead, they will smell and appear shriveled and rotting.
Take a closer look at the roots in the center and if they look healthier, then cut off the rotting sections and replant the viable roots into a fresh pot with barely damp soil.
Plants that look a bit dreary, often with no leaves, could be in a state of dormancy and waiting for warmer weather to expand and grow into healthy and beautiful plants once the weather warms.
What happens when houseplants go dormant?
When houseplants go dormant, the leaves will turn yellow. There will be less foliage growth and shedding of leaves. The houseplant may even look like it’s dead, but the roots will be alive.
Dormancy is a natural part of plants’ growing cycle, but this happens more subtly for houseplants. Houseplants respond to the change in temperature and light by slowing down in growth.
Houseplants lose a small number of leaves and often with temperatures dropping, some leaves may also wilt. They stop growing, however, the root system will often be thriving and healthy during dormancy. -Tammy Sons, Owner, Tn Nursery
In the winter months, there is less sunlight shining through the windows. The plants will photosynthesize less, which causes them to slow down.
Although houseplants have slowed down in growth during dormancy, they are still preparing for new growth in the spring. Plants break down and remake proteins and maintain and strengthen cell membranes needed to expand and multiply when the temperature is warmer.
How do you care for dormant plants in the winter?
Houseplants and plants brought indoors for winter and living in a temperature-controlled setting are still affected by changes to their environment.
These dormant plants must contend with fluctuating temperatures, changing from warmer in the daytime to colder at night, drier air, shorter days, and little light.
Caring for and supporting your plants during their time of rest will keep them happy and thriving, and you will be rewarded with healthy plants in the new season.
Do plants need light when dormant?
Plants need light when dormant but less than what they would need otherwise. This is because their growth has slowed down. All plants require sunlight for photosynthesis to manufacture carbohydrates into energy.
Houseplants may become floppy and leggy with weak stems if they have inadequate light.
If there is insufficient sunlight, consider using artificial light such as a fluorescent light shining near but not directly on the plant.
It depends on plants and if you have artificial light and heat. I have some that I put outside to go dormant.. and others that I use heat and lights to keep growing. – Micah
Do dormant plants need water in winter?
Dormant plants require less water during winter when they experience slower growth and needless hydration. Avoid overwatering, which could lead to root rot.
Plants that grow in direct sunlight become drier on the surface, but the soil beneath could still be moist. Test the soil one or two inches from the surface, and if it is dry, then water the plant.
Avoid shocking the roots when hydrating houseplants in winter by allowing the water to reach room temperature.
Should dormant plants be fertilized?
Dormant plants should not be fertilized as this could cause new growth that won’t be able to survive the cold weather. The dormant plants don’t need much nutrition as they are not actively growing.
Fertilizing during the dormant stage can affect the plant’s overall health as the unused fertilizer may accumulate in the soil, burn the roots and damage the whole plant.
Can you stop a houseplant from going dormant?
You can stop a houseplant from going dormant by providing the required light, warmth, humidity, and nutrients. You can provide light using a grow light. You can provide the necessary heat by using heating mats. You can move them to a location that is warm such as the kitchen.
Houseplants can be forced to grow all year round; however, plants do need a period of rest to remain healthy, so be sure that the plant will cope with the forced growth.

Fact Checked, Written, and Published by Kevin Rodrigues
Kevin is the founder of Gardening Mentor, a website that aims to teach people to grow their own food in a limited space. As a self-taught gardener, Kevin has spent several years growing plants and creating gardening content on the website. He is certified in Home Horticulture and Organic Gardening from Oregon State University. He has a Post Graduate Diploma in Horticulture and Landscape Gardening from Mumbai University.
Read more
